why competing across national borders makes strategy-making more complex:
- maintain a national product base and export goods to foreign market.
- license foreign firms to produce and distribute the company product abroad.
- employ a franchising strategy.
- establish a subsidiary in a foreign market via acquisition or internal development.
- rely on strategic alliances or joint ventures with foreign companies.
there is three main strategic approaches in competing internationally.
multi domestic strategy
it strategy is matches to local market needs- think local, act local. different country strategies are called for when
- significant country-to-country differences in customer need exist
- buyers in one country want a product different from buyers in another country
- host government regulations preclude uniform global approach.
two drawbacks
- poses problem of transferring competencies across borders
- works against building a unified competitive advantage

Multi domestic Approach
(think local, act local) |
|
advantages
|
disadvantages
|
Can meet the specific
needs of each market more precisely
|
Hinders resource and
capability sharing or cross-market transfers
|
Can respond more
swiftly to localized changes in demand
|
Higher production and
distribution costs
|
Can target reactions to
the moves of local rivals
|
Not conducive to a
worldwide competitive advantage
|
Can respond more
quickly to local opportunities and threats
|
|
global strategy
strategy for competing is similar in all country markets- think global, act local
involves
- coordinating strategic moves globally
- selling in many, if not all, nations where a significant markets exists.
work best when product and buyer requirements are similar from country to country

Global Approach
(think global, act global) |
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Lower costs due to scale and scope economies
|
Unable to address local needs precisely
|
Greater efficiencies due to the ability to transfer best practices
across markets
|
Less responsive to changes in local market conditions
|
More innovation from knowledge sharing and capability transfer
|
Higher transportation costs and tariffs
|
The benefit of a global brand and reputation
|
Higher coordination and integration costs
|
transnational strategy
incorporates elements of both of globalization and localization approach to strategy making- think global, act global.
Transnational Approach
(think global, act local) |
|
advantages
|
disadvantages
|
Offers the benefits of both local responsiveness and global
integration
|
More complex and harder to implement
|
Enables the transfer and sharing of resources and capabilities across
borders
|
Conflicting goals may be difficult to reconcile and require
trade-offs
|
Provides the benefits of flexible coordination
|
Implementation more costly and time-consuming
|
that all for chapter 7...bye JJJ

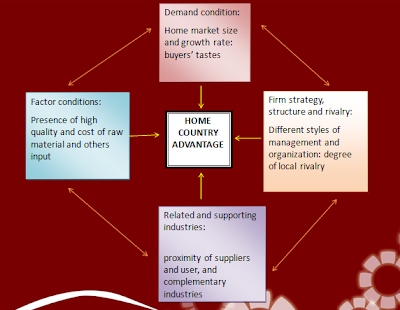



.jpg)
0 comments:
Post a Comment